Module 1: Market Information
By the end of this module, you will have covered:
- Who equine customers and consumers are.
- The category size and value.
- Typical purchase behaviour.
- An overview of category management aims and principles.
Data sources:
BETA National Equestrian Survey 2024
SPILLERS™ Bi-annual Tracker Survey 2024 (n=1,002)
Market Size
- 726k estimated number of households in Great Britian that own or care for a horse.
- 631k privately owned horses in Great Britian
- 1.82m regular riders.
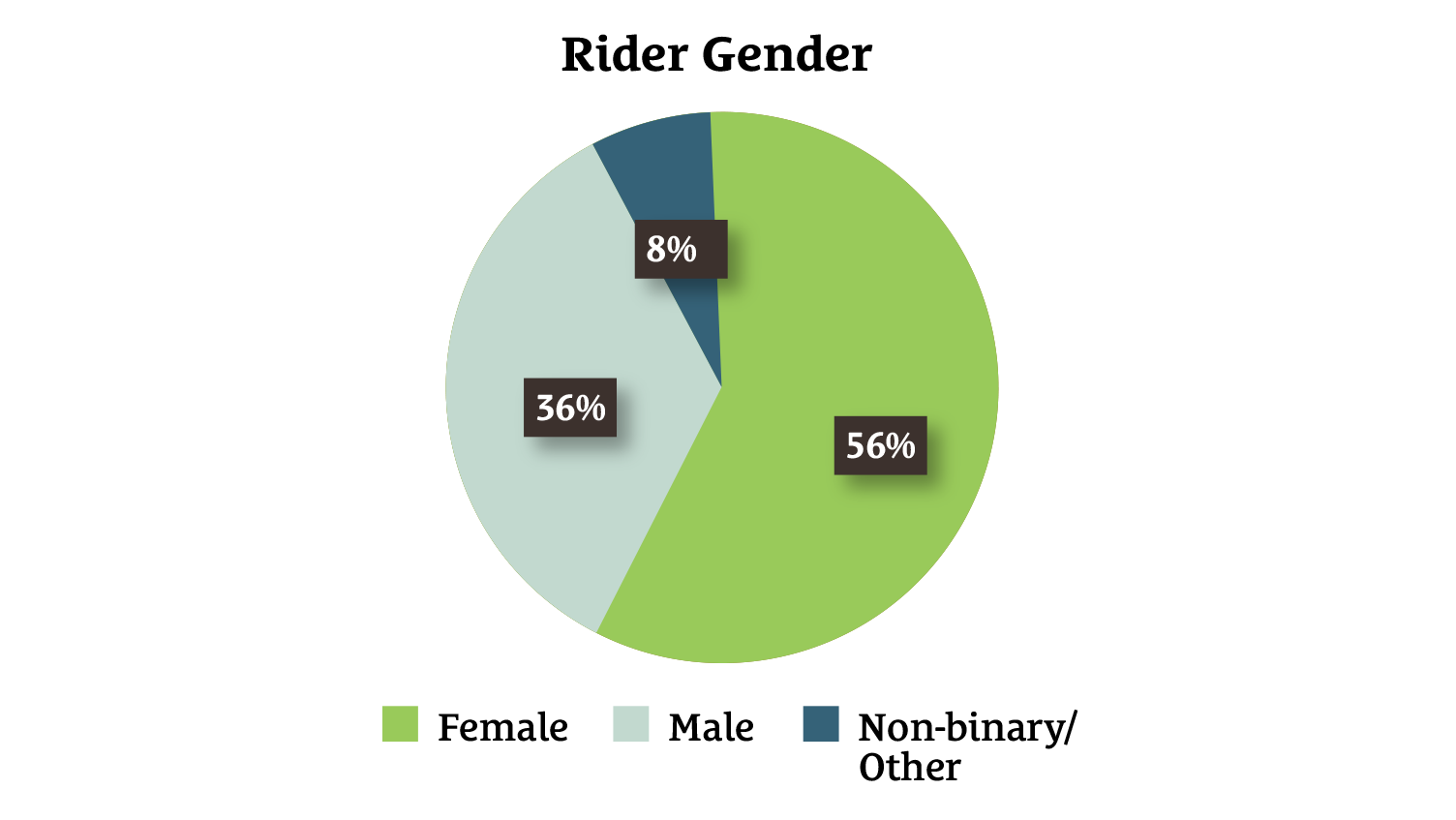
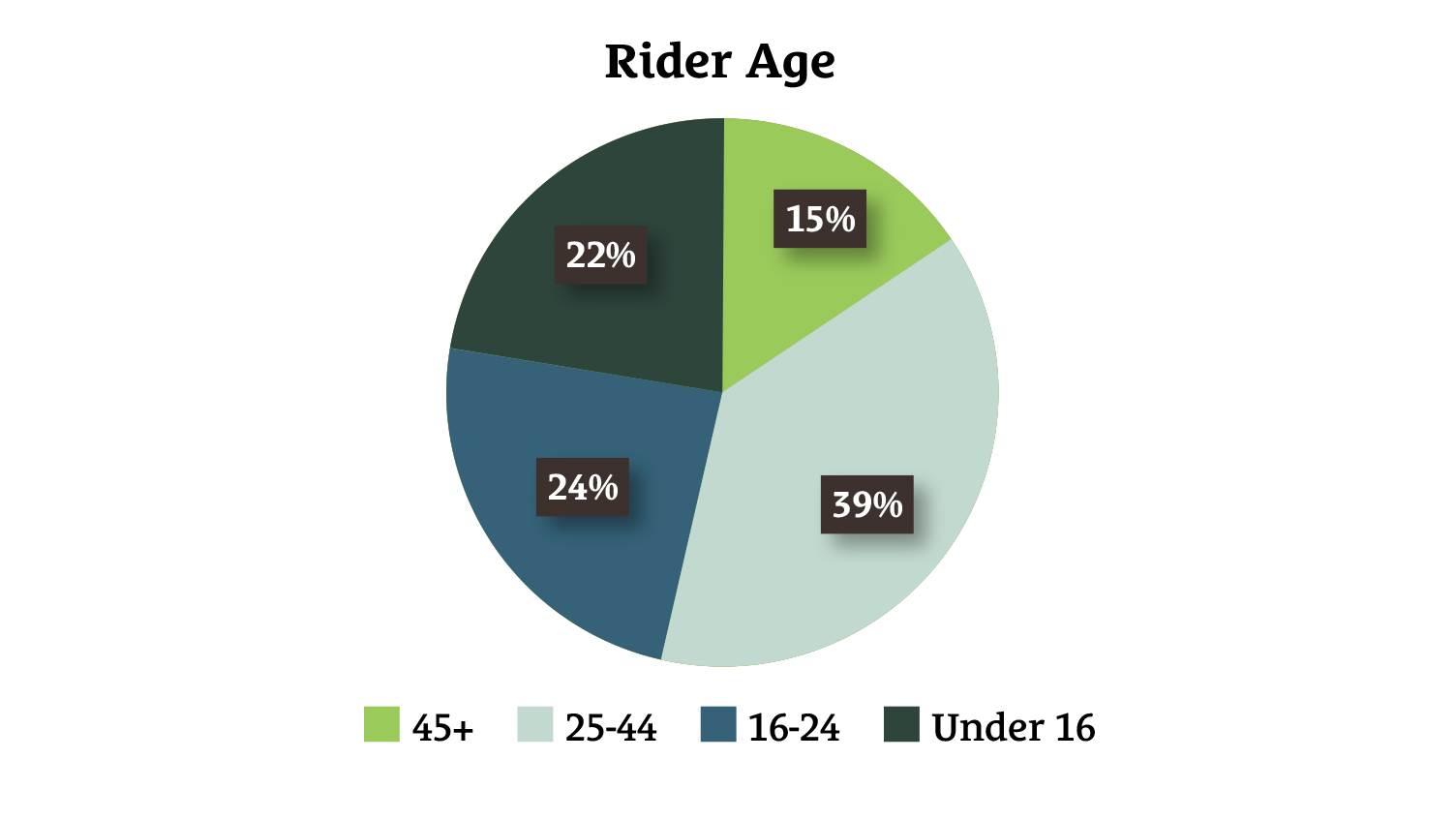
Spend of feed
- £252m annual spend on feed

A typical customer
- Checks the feed they buy meets the following criteria in this priority order:
- Is a suitable nutritional profile for their horse
- Is low in sugar and starch
- Is molasses free
- Is a good price
- The estimated average spend on manufactured feed is £306 per annum.
- The average value per order is £39 / volume per order is 38kg.
Category Management
Is simply defined as different tactics used to change shopper behaviour to grow the category. In 2023, 90% of Mars’ growth came from category growth – 10% came from gaining share.
There are 3 drivers for category growth…
Increase penetration
Increase basket size
Increase basket spend
How to influence… ABC
ATTRACT the Shopper via effective Point of Sale
- Increase Penetration by ATTRACTING new customers to sub-categories they may previously not have bought.
- Drive trade up by highlighting targeted products that better suit the horse’s individual needs.
Make the Shopper BROWSE via effective Merchandising
- Increase BASKET SPEND by exposing shoppers to higher average selling price products.
- Increase BASKET SIZE by exposing shoppers to impulse purchases.
CONVERT the Shopper via effective Ranging
- Increase BASKET SIZE by maximising market coverage.
- Increase basket SPEND by including clear trade ups within range.
- Improve range efficiency.

Attract
- Use POS to highlight USPs to drive trade up.
- Use POS to create in store theatre. Shoppers tend to spend longer browsing in nicer shopping environments.
- If there is no physical product instore use range boards so customers can see what products are available.
Browse: What to consider before relaying
1. Consider traffic flow around the store. Studies have shown that people naturally go to the right when they enter a store. Use this to your advantage by placing high ASP or impulse purchases in these areas
2. Use HOT SPOTS to communicate promotions for greater impact
3. Locate related categories nearby
4. Locate VALUE towards back of store to pull customers further in
5. Create breaks. Long uninterrupted aisles are off putting as shoppers find it harder to navigate the range
6. Avoid bottlenecks. Shoppers don’t like feeling trapped, they will avoid bottlenecks meaning that either that area of the stores gets ignored
7. Avoid blocking the eye line as this will improve navigation around the store
8. Place Fibres higher in racking than Compounds as plastic is less likely to be damaged when handling
9. Make sure BESTSELLERS are easy to replenish as out of stocks will impact sales more than layout
10. Consult the warehouse team when making any changes to store layout
Convert: Conducting a range review

Know;
- Retailer strategy- What are you trying to achieve? (Increasing: Penetration, Basket Size, Basket Spend)
- Merchandising space - What is the maximum number of display slots available? This will determine range size.

Understand;
- Category Trends -Which sub-categories are growing as you will want to over-index in the space you allocate to take advantage of the growth opportunity
- Segmentation - What are the different partitions that you need to cover to maximise choice?

Prioritise:
- Brand success – Which brands can boost your growth with their momentum?
- Supplier service - Which suppliers provide excellent customer service for efficiency and availability?
- Supplier support - Which suppliers are backing you to generate demand for their products?
Establish criteria:
- Purchase frequency - How often does the product bring shoppers to the store?
- Financial goals - Is the product meeting your Volume, Value, and Margin targets?
- Complaints/Expired stock - What percentage of sales or stock results in complaints or expiration issues
Congratulations
You have now completed Module 1 and should now have a better understanding of the typical horse owner, their purchase behaviour and some basic principles for effective category management.
You can now move on to Module 2 which will take you through Naturally Occurring Prohibited Substances (NOPS).
